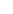
R&D
R&D
Production Line
Marking of Grinding wheels
- WAⓐ
- 60ⓑ
- Jⓒ
- 6ⓓ
- Vⓔ
- 1A
ⓐ Abrasives wheels manufactured according to the manufacturing method
- A = Alundum
- WA = White Alundum
- GC = Green Carborundum
- SG = ∝-Al2O3 manufactured by the sol-gel method
- PA = Pink Alundum
- SA = Single Crystaline Alundum
- C = Carborundum
ⓑ Represents a particle size of 60 mesh (250㎛)
- Assembly = 10 ~ 24mesh
- Fine grain = 80 ~ 220mesh
- Neutrality = 30 ~ 60mesh
- Microfine = 240 ~ 800mesh
ⓒ Bonding degree of grinding wheels
- E, F, G = the most soft
- I, M, N, O = Medium
- T, U, V, W, X, Y, Z = very hard
- H, I, J, K = soft
- P, Q, R, S = hard
ⓓ Organization of grinding wheel
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compactness | Normal | Sloppy | |||||||||||
ⓔ Type of bond
- V = Vitrified
- B = Resinoid
Foundation of Grinding wheels
Components of grinding wheels
- 1. Abrasive : The role of cutting the workpiece with the cutting edge.
- 2. Binder : The role of binding and protecting the abrasive grains.
- 3. Pore : It is between the abrasive grain and the binder, and the role to escape the cutting powder.
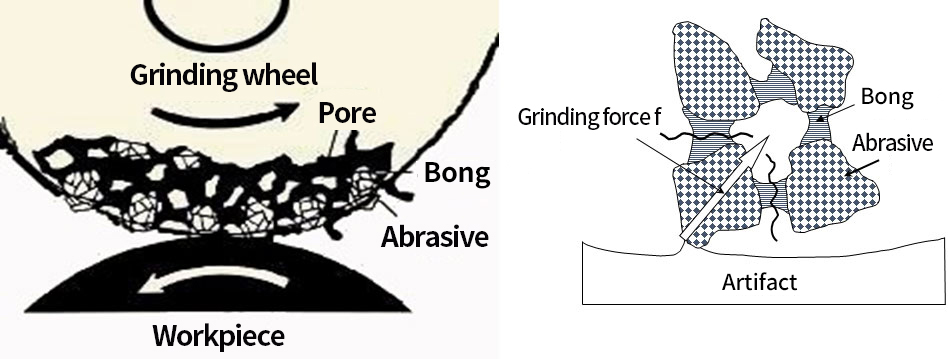
[ The location of the elements that make up the grinding wheels ]
Type and characteristics of grain
Abrasive
Abrasive is an artificial synthetic material that acts as a cutting edge in a grinding wheel.
| Type | Color | Mark | Name | Manufacturing method | Usage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic abrasive (AI203) | Blue (opaque) | SS | CUBITRON | Ceramic inorganic material produced through the SOL-GEL process (process) | Grinding of difficult-to-cut materials such as soft, high carbon steel and stainless steel | |
| White (opaque) | SG | HTB | ||||
| Silicon carbide (SiC) | black | C | Black Silicon Carbide | Crystallization of silica and carbon material by crystallization in an electric resistance furnace | Casting, non-metal, abrasive cloth, refractory, crystal, stone | |
| Green | GC | Green Silicon Carbide | It is made by crystallizing a carbon material having a higher purity than the raw material by the same method | Cemented carbide, refractory | ||
Types and characteristics of abrasives
| Type | Color | Mark | Name | Manufacturing method | Usage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molten alumina (Al2O3) | Brown | A | Regular Aluminium Oxide | Brown crystals pulverized by melting bauxite in an electric furnace | General steel, grinding cloth, optical grinding, semiconductor grinding, refractory, etc. | |
| White | WA | White Aluminium Oxide | Crystal by melting and pulverizing alumina by the Basya method | Synthetic steel, abrasive paper, special refractory, etc. | ||
| Light gray | HA | Single crystal Aluminium Oxide | An incoat made by adding and dissolving sulfur, etc. to an alumina compound is submerged in water and separated by particles | Light grinding tool steel of alloy steel, special steel | ||
| MA | ||||||
| 32A | ||||||
| SA | ||||||
| Pink | PA | Pink Aluminium Oxide | Same as WA product, but melted and crystallized by adding a little Cr203 to give it properties | Internal grinding and gear grinding of general heat treated steel | ||
| RA | ||||||
| Brown | TA | Collection of grains (集結晶砥粒) | It is the same as the manufacturing method of brown molten alumina grinding material, but makes the crystal large by making a difference in the cooling speed. | Slab Billet Heavy Duty grinding | ||
| Gray | Z | Zirconia Aluminium Oxide | Alumina and zirconia are mixed and pulverized by melt cooling under special conditions | Super heavy grinding of steel, casting, and steel | ||